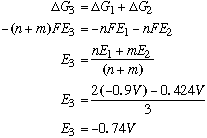Thermodynamics Solutions: #31
31.* (1992 2 6) A. Using the standard reduction potentials below, deduce the standard potential of the following reaction which occurs in aqueous solution: 2Fe3+ + 2I- --> Fe2+ + I2.
Note: It is OK to add voltages in this case because we are dealing with a balanced reaction. However, if we were dealing with a half-reaction, you'd have to convert to free energy values. (DGo=-nFEo) B. Using the standard reduction potentials below, deduce the standard potential of the reduction of Cr(III) to Cr metal.
This is a half-reaction, so we have to convert to free-energy values:
|