Thermodynamics Solutions: #9
9.* (1996 3 2) Consider the thermodynamic factors underlying the polymerization of a simple olefin: propylene. A. Calculate the value of the enthalpy change DH° (the bond energies of a carbon-carbon sigma bond and a carbon-carbon p bond are approximately 86 and 63 kcal/mol, respectively).
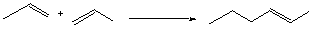
For each monomer entering the polymer: break one p bond: DH = +63 kcal/mol form one s bond: DH = -86 kcal/mol –––––––––––––– DH = -23 kcal/mol
B. Give the sign of the enthalpy change for the polymerization. The sign of the DH term is negative, so the reaction is enthalpically favorable and exothermic. C. Deduce the sign of the entropy change for this reaction. DS, the change in entropy, is negative because we’re putting all the monomers together to make a polymer, which is more ordered than free molecules. D. What is the sign of the Gibbs free energy change for this reaction? Explain your reasoning and show your calculation. DG = DH -TDS = -23 kcal/mol - (298)(something negative) DG will be negative as long as the TDS term is less than 23 kcal/mol (i.e. DG is negative except at high temperature.) We know that polypropylene is formed from propylene, so DG must be negative under relatively ordinary conditions, so |DH| > |TDS| 
|