Thermodynamics Solutions: #15
15.* (1995 F 8) The following are the four bases found in DNA.
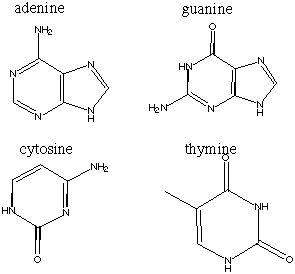
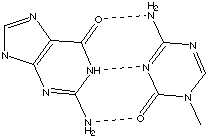
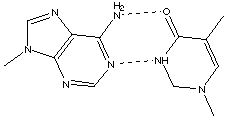
A. Draw the complementary base pairs indicating their hydrogen bonding.
B. The double-stranded helical structure of DNA is maintained primarily by the hydrogen bonds, which are weak bonds. With increasing heat, the double-stranded DNA can separate into single strands in a process called denaturation or "melting." The melting temperature Tm is defined as the temperature at which half the helical structure is lost. The abruptness of the transition indicated that the DNA double helix is a highly cooperative structure held together by many reinforcing bonds. Predict how the melting temperature varies with the base-pair composition in DNA for a given number of bases. G-C base pairs have 3 hydrogen bonds, while A-T base pairs have two. Therefore, double-stranded DNA with a higher number of G-C base pairs will be more strongly bonded together, more stable, and will have a higher melting temperature. |