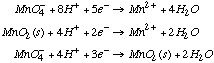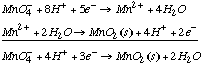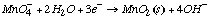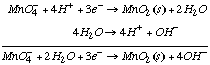Thermodynamics Solutions: #11
11.* (1996 3 6) You are given the following reactions with their standard potentials as shown.
A. Find E°3. We can add add half-reaction (1) and the reverse of half-reaction (2) to obtain reaction (3), but because we are dealing with half-reactions, we cannot simply add the voltages afterwards. We must convert to free energy units. DG° is a state function, but DE° is not.
Doing the calculation in terms of free energy ( DG=-nFEo):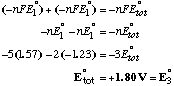
B. What is E°4 for the same reaction as (3) but run under basic conditions rather than acidic conditions? The new half reaction is:
We can obtain reaction (4) by adding reaction (3) to the equation H2O–>H++OH-:
Because źG°=-nFE°, 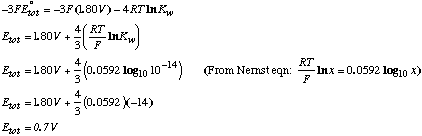 |