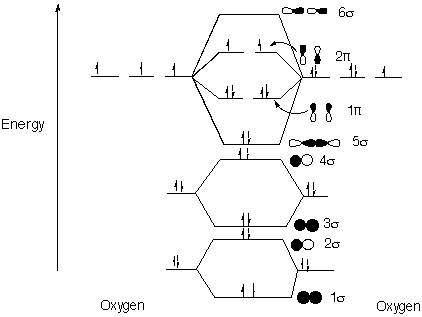
Structure and Bonding Solutions: #55.* (1996 F 7) Four oxidation state of molecular dioxygen are known: [O2]n where n= 0, +1, -1, -2. They are dioxygen, dioxygen cation, superoxide anion, and peroxide dianion, respectively. The O-O distances and infrared stretching frequencies have been measured for these four oxidation states. A. Draw a MO diagram for O2 and fill in the electrons.
B. Fill in the correct value of n for the bond distances and the infrared stretching frequencies in the table below.
When electrons are added (forming the negatively charged anions), they are added to an antibonding orbital, decreasing the bond order and destabilizing the molecule. When electrons are taken away (forming the positively charged cation), they are taken away from an antibonding orbital, increasing the bond order and stabilizing the molecule. Recall that greater bond order correlates to shorter bond length and larger stretching frequency.
C. Which is these O2 derivatives is diamagnetic (no unpaired electrons)? O22- is diamagnetic because the two extra electrons pair with the electrons currently in the p* orbitals.D. Which of these compounds is paramagnetic (has unpaired electrons)? All the compounds except O22- are paramagnetic. |