Organometallic Solutions: #17
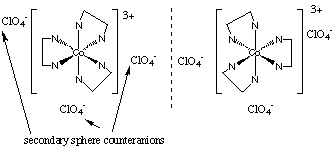
17.* (1992 F 25) Consider the diamagnetic complex [M(en)3(ClO4) 3] where M is a 3d metal. A. What is M? M is Co (which is d6 in its III oxidation state.) B. What is the oxidation state of M? The oxidation state is III, because each ClO4- has a -1 charge. This way, we can also have a low-spin system. C. How many d electrons? There are 6 d electrons. D. Will this complex be a strong oxidizing agent? To be a strong oxidizing agent the complex must gain electrons easily. However, any electrons this complex gains will go into the high energy eg antibonding orbitals. Therefore, this compound won't be a strong oxidizing agent. E. Sketch a picture of all stereoisomers of this complex.
F. What features would the 13C NMR spectrum exhibit? The 13C NMR of the racemic mixture would show a single peak. This peak would be a triplet in high-resolution proton-coupled spectra due to the effects of the 2 hydrogens attached to each C, but would be a singlet in the proton-decoupled spectra. (Note: the spectrum of a pure enantiomer would be the same. NMR cannot distinguish between enantiomers!) |