Coordination Chemistry Solutions: #1
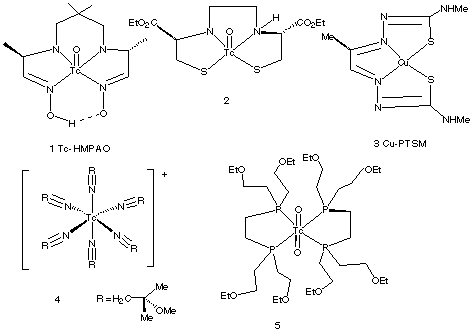
1.* (1997 F 4) Certain coordination compounds are used in clinical medicine as heart and brain imaging agents. A selection of these is shown below (from "Chemistry in Britain", October 1994, P. 820).
A. Indicate which compounds are chiral. (assume the two oxo groups in (5) are trans.). Write the compound numbers for any chiral compounds you find in Figure 2. #1 and #2 are chiral. B. Compound 2 enters the brain by diffusing through the brain blood barrier; this substance is trapped because it is acted on in the brain by an esterase. A stereoisomer of 2 is not trapped in the brain. Propose a plausible explanation of this fact. One chiral stereoisomer is acted on by the esterase. The selective, chiral enzyme does not interact with the other stereoisomer of 2; therefore 2 is free to diffuse back through the brain blood barrier. C. What is the oxidation state of copper in compound 3? Predict the coordination geometry, and d-electron configuration for 3. 2+. The compound is d9, square planar. D. What is the oxidation state, d-electron configuration, and number of unpaired electrons in compound 4? 1+. The compound is d6 and has no unpaired electrons. |