NMR Part 1 Solutions: #4
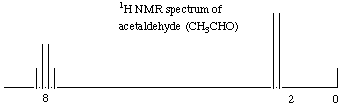
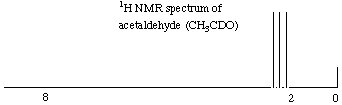
4.* (1996 2 5) The accompanying figure displays the 1H NMR spectrum of acetaldehyde, CH3CHO, measured at 60 MHz. By writing on the spectrum define the following quantities: A. chemical shift. B. spin coupling C. upfield (increasing magnetic field) D. Assign the peaks in this spectrum to their counterparts on the structure of acetaldehyde. E. In the space provided below sketch the proton NMR spectrum you expect for deuteroacetaldehyde: CH3CDO (recall that deuterium has a nuclear spin quantum number of 1).
A. Chemical shift refers to the amount that a peak on an NMR spectrum is displaced from some standard, which is usually tetramethylsilane (TMS). B. Spin coupling refers to the amount by which the electron spin of adjacent atoms affects the magnetic field felt by a given atom. C. Upfield (increasing magnetic field) is the direction to the right on the NMR spectrum. If an atom does a spin flip high upfield (far to the right), then it must be very shielded, because a high magnetic field was required to produce the spin flip. D. Shown on the spectrum below.
E. Protons have a nuclear spin quantum number of 1/2, which means that they can have 2*1/2 + 1 (or 2) possible orientations in a magnetic field. On the other hand, deuterium has a nuclear spin quantum number of 1, which means that it can have 2*1 + 1 (or 3) possible orientations in a magnetic field. Therefore, where one adjacent proton would split its neighbor’s signal into a doublet (because of its two possible orientations), one adjacent deuterium would split its neighbor’s signal into a triplet (because of its three possible orientations). The spectrum you would get is shown below. Note that the deuterium would not show up in this spectrum because it is the proton NMR spectrum. Deuterium resonates at frequencies that are far off the proton NMR scale. Note also that the three peaks of the triplet are the same height. This is because there is no degenerate state in which one H up and one H down is the same as one H down and one H up (which makes the middle peak twice as high in a triplet generated by protons). There are simply three states that the D can be in, so all peaks are the same height.
|